
Legal barriers to entry into a monopolistic industry also exist in the form of patents and licenses. Government usually gives one firm the right to operate a public utility industry in exchange for government regulation of its power. Public utilities are often natural monopolies because they have economies of scale in the extreme case where one firm is most efficient in satisfying the entire demand. Google and Amazon both enjoy economies of scale in their respective markets.
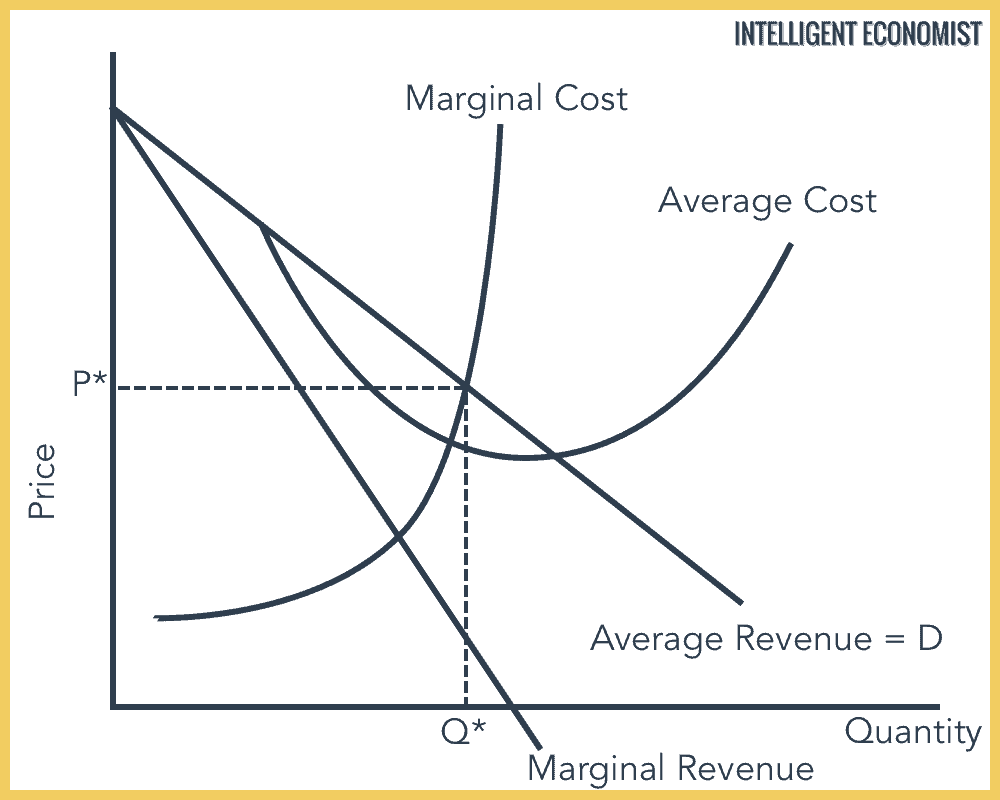
Because a very large firm with a large market share is most efficient, new firms cannot afford to start up in industries with economies of scale. This occurs where the lowest unit costs and, therefore, lowest unit prices for consumers depend on the existence of a small number of large firms or, in the case of a pure monopoly, only one firm.

The Last Word examines how some Internet companies have achieved near monopoly power due to network effects and economies of scale.Įconomies of scale constitute one major barrier. Some basic issues involved in the regulation of public service monopolies are reviewed. This section ends with a discussion of the effects of monopoly power in the U.S. The case of price discrimination and its effects are discussed along with the conditions necessary for it to occur. The misconceptions about monopoly pricing behavior are presented, as well as a comparison of efficiency in pure competition and pure monopoly. Emphasis here is on the major difference between the determination of marginal revenue in pure competition and in pure monopoly. The concept of a natural monopoly is addressed in this section.īuilding on the analysis of the preceding chapter, the discussion of the price‑output decision-making by monopoly firms points out that the marginal-revenue=marginal-cost rule still applies. The discussion of barriers to entry asserts at the outset that these barriers may occur to some extent in any form of imperfect competition, not just in a pure monopoly. This chapter is divided into seven learning objectives: the characteristics of pure monopoly, the barriers to entry that create and protect monopolies, how demand is viewed by a monopolist, price and output determination under monopoly, the economic effects of monopoly, price discrimination, and the regulation of monopolies.

No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
